LESS THERMAL BRIDGING
R-stud outperforms the generic steel stud on thermal performance, allowing for 40% less thermal bridging. With more emphasis being placed on building performance, the R-stud provides an excellent R value compared to its competitors, addressing thermal bridge concerns effectively.
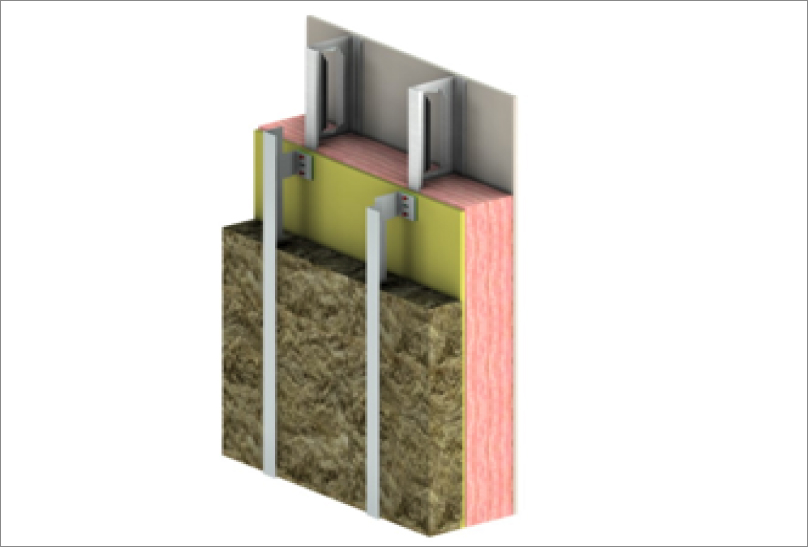
MH 3D THERMAL MODELING OF STEEL FRAMED WALLS
The thermal performance of the Nvelope/R-Stud Systems were evaluated by 3D thermal modelling using the Nx software package from Siemens, which is a general purpose computer aided design (CAD) and finite element analysis (FEA) package
The thermal solver and modelling procedures utilized for this study were extensively calibrated and validated for ASHRAE Research Project 1365-RP Thermal Performance of Building Envelope Details for Mid- and High-Rise Construction and for the Building Envelope Thermal Bridging Guide1.
The clear field U-values (U) were determined using the methodology presented in these two documents. The thermal analysis utilized steady-state conditions, published thermal properties of materials, and information provided by SFS Group USA.
RDH BUILDING SCIENCE LABS- THERMAL TESTING
- 1. Several assembly mock-ups testedd
- 2. Guarded hot plate apparatusd
- 3. Use of several materialsd
- a) Steel framingd
- b) Gypsum sheathingd
- c) Insulation (Roxul/Thermafiber)d
- d) Interior GWBd
- e) Polyethylene foam (2.4mm)d
- 4. Mineral wool Guard at edgesd
- 5. Core assembly of 32' X 32"d
- 6. Nine separate specimensd
- 7. Conventional and R-stud comparisonsd
- 8. Additional insulation types (glass)d
- Conclusion: approx 35% improvement in R-Value was realized when campared to conventional steel studs of the same mil thickness.d
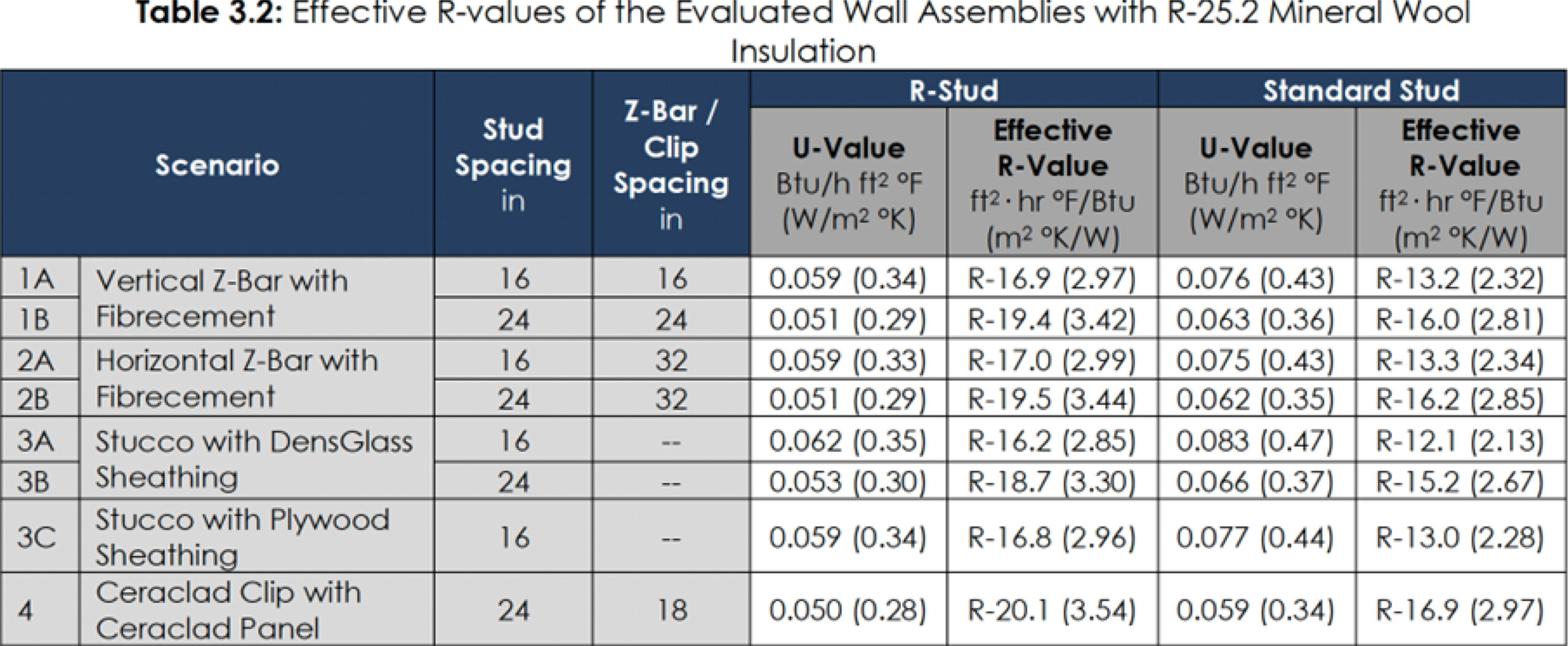
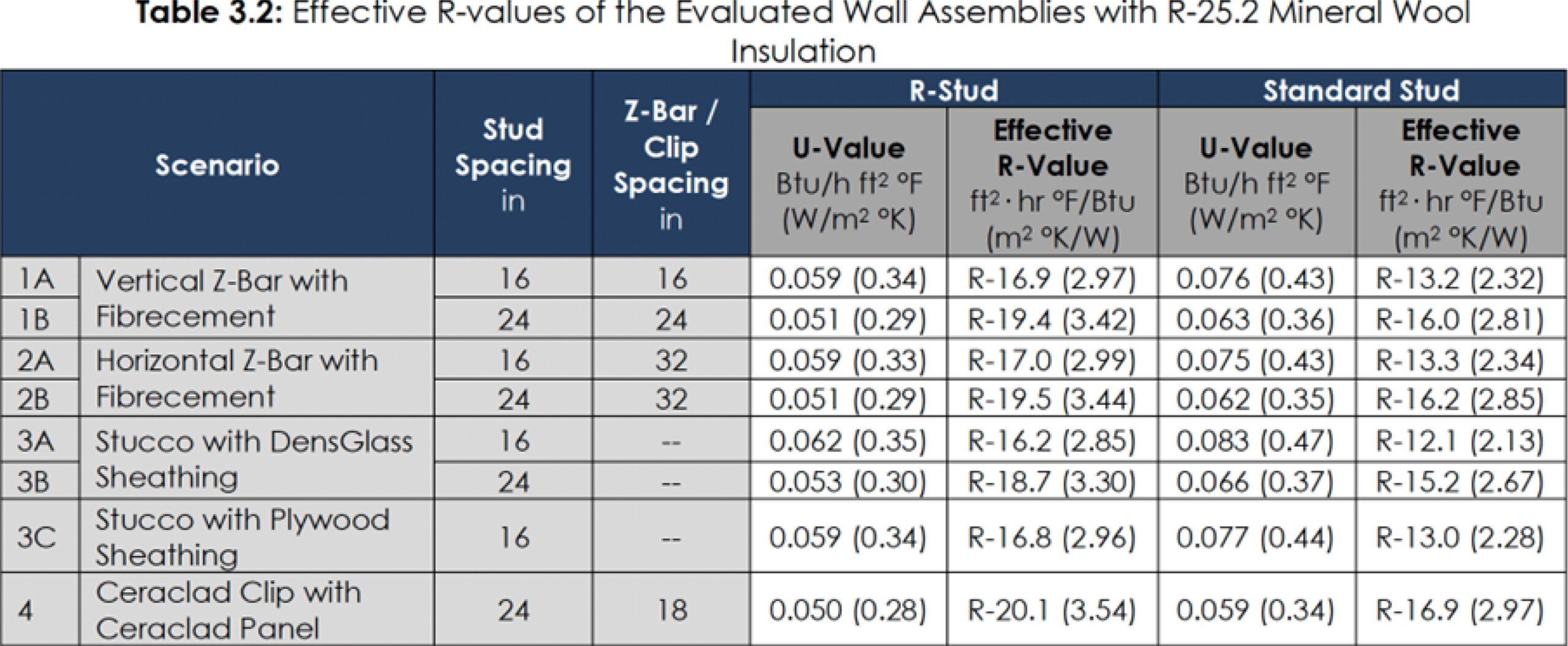
LOWER OPERATIONAL CARBON USING R-STUD
THERMAL
40% Reduction in thermal bridging over standard steel studs.
26% Greater R-value (material resistance to thermal energy transfer) with fiberglass batt insulation and 35% higher R-value with blown fiberglass insulation compared to standard studs.
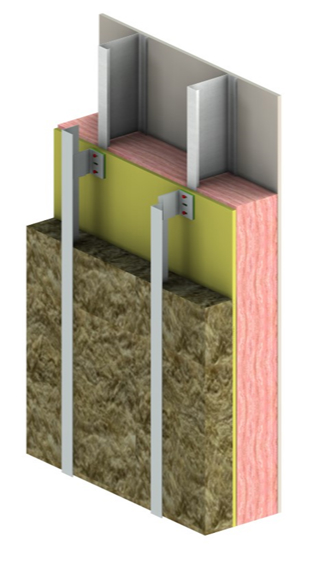
VS
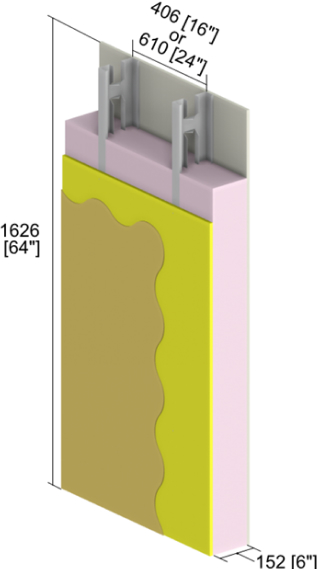
Standard stud assembly vs R-stud assembly


